Cancer is a disease that can affect many facets of a person’s life, from physical effects to emotional challenges. Among the side effects of cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy and hormone therapy, joint pain or “arthralgia” is frequently reported.
Origins of Post-Chemotherapy Arthralgia
According to recent studies, arthralgia can be caused by medications used to treat cancer, including chemotherapy. Lung cancer patients, for example, have reported cases of arthralgia and arthritis following chemotherapy. This is not only limited to lung cancer patients. Women who have battled breast cancer have also reported muscle and joint pain.
The causes of this pain can vary: presence of bone metastases, secretion of inflammatory mediators by a tumor, or pressure exerted by a tumor on neighboring organs. These pains can be transient or chronic, and their intensity can vary from mild to severe. For some patients, the pain can even disrupt basic daily activities.
Managing Pain
Fortunately, there are ways to manage and relieve joint pain:
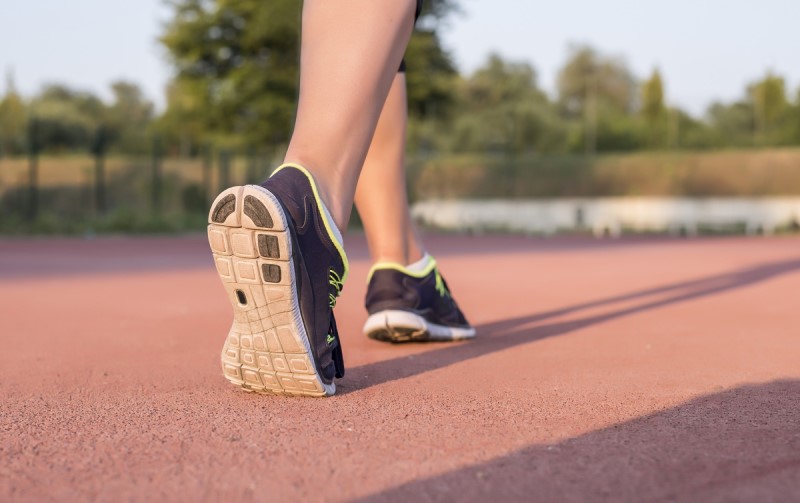
- Appropriate physical activity: Getting moving can help reduce pain. Stretching and gentle exercises, such as yoga, can improve flexibility and reduce stiffness. Moreover, staying active can also help maintain a healthy weight, which can reduce pressure on the joints.
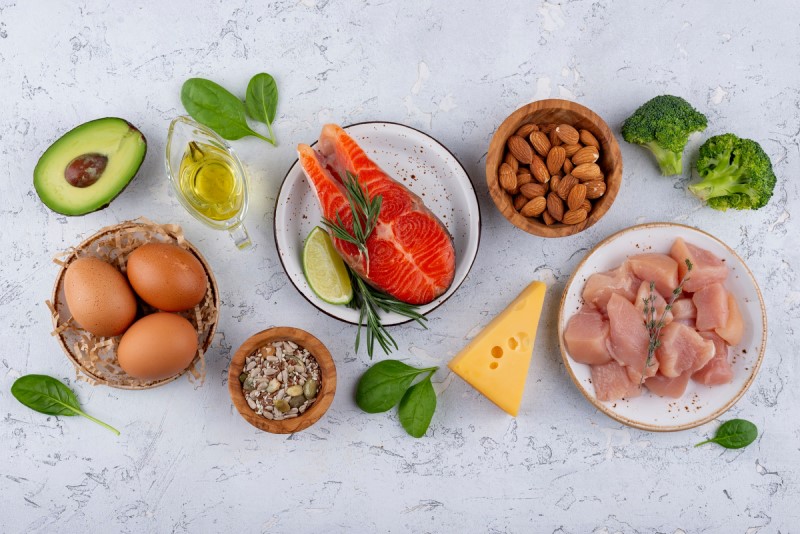
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These fatty acids have anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 into one’s diet, such as fatty fish (salmon, tuna, sardines), nuts, and various seeds, can help relieve joint pain.
- Managing stress: Pain can be exacerbated by stress. Finding ways to manage one’s stress, whether through meditation, relaxation, or other techniques, can also help reduce the perception of pain.
Conclusion
Joint pain can be a confusing and disturbing side effect of cancer treatments, but it is not insurmountable. By understanding its origin and adopting appropriate management strategies, it is possible to mitigate its effects and improve quality of life.
References: