Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a growing health concern worldwide. It is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver and is often associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. When NAFLD progresses to inflammation and liver cell injury, it becomes non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NASH can lead to liver fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer. In this blog post, we will discuss the risk factors associated with NASH.
Age and Gender : According to a recent study published in Frontiers in Nutrition, age and gender are two factors that play a role in the development of NASH. The study found that the prevalence of NASH increased with age, with the highest rates observed in individuals over 60 years old. Furthermore, the study found that men were more likely to develop NASH than women, with a male-to-female ratio of approximately 2:1.
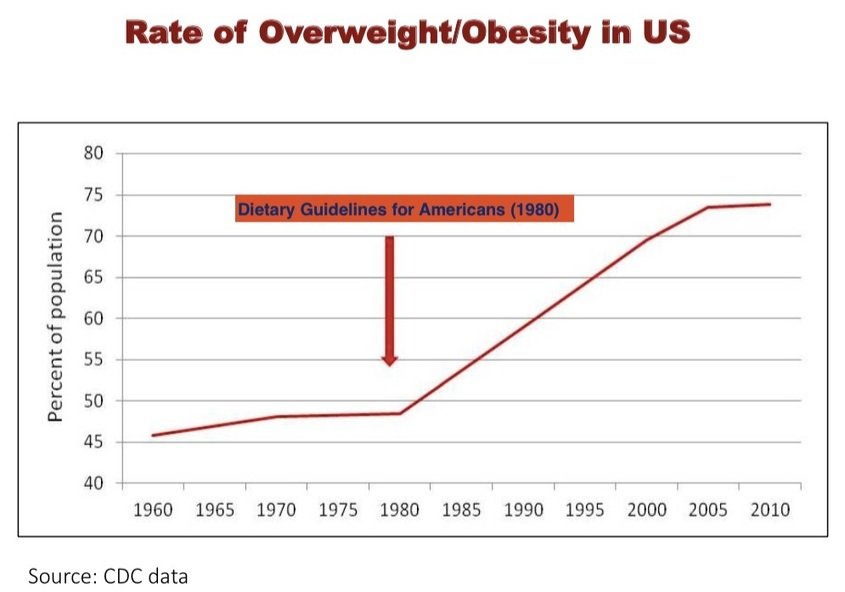
Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome : Obesity is one of the strongest risk factors for NASH. A study published in the Journal of Translational Internal Medicine found that individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher had a significantly higher risk of developing NASH compared to those with a lower BMI. Metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that includes high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol or triglyceride levels, is also strongly associated with NASH.
Type 2 Diabetes: Individuals with type 2 diabetes have a higher risk of developing NASH compared to those without diabetes. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that individuals with type 2 diabetes were more likely to have liver fibrosis and inflammation, two hallmarks of NASH.
Genetic Factors: While lifestyle factors such as obesity and metabolic syndrome play a significant role in the development of NASH, genetic factors may also contribute to the risk of developing the disease. A study published in the Journal of Hepatology found that certain genetic variants were associated with an increased risk of developing NASH. Specifically, the study found that a variant in the PNPLA3 gene (gene providing instructions for making a protein in fat cells and liver cells) was strongly associated with the development of NASH.
Individuals with one or more of these risk factors should be screened for NASH, and lifestyle modifications and medical interventions should be considered to reduce the risk of developing the disease.
“DietSensor Nash” for iOS (download here) is a nutrition coaching app specialized in Nash to help patients affected by the disease tackle and if possible reverse it. It provides daily guidance, meal plans, a meal generator to match your preferences, nutrition education, macronutrient tracking, and a chat with a dietitian. It starts at the price of $49 to make sure anybody has access to its science-backed content.
References:
https://www.the-nash-education-program.com/what-is-nash/who-is-at-risk-for-nash/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1665268122000692
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2020.00071/full