When it comes to managing diabetes, nutrition plays a vital role. In this article, we’ll explore the foundations of nutrition and guidelines that can help individuals with diabetes to maintain their health. We will focus on an article published in Diabetes Care: click here to access the full article.
The article begins by highlighting the importance of glycaemic management. This consists of monitoring blood glucose levels to keep diabetes in control, or to identify any imbalance, and avoid potentially major health issues. Diet plays key role in this process.
One of the fundamental principles of nutrition for people with diabetes is to monitor carbs intake. Carbs have a direct impact on glycemia, as they are converted into glucose in the body. The article advocates the consumption of complex carbs, such as wholegrain cereals, vegetables and legumes, which have a more gradual effect on blood glucose levels than simple carbs, like sweets and soft drinks (now more commonly referred to as high, medium or low glycemic index).
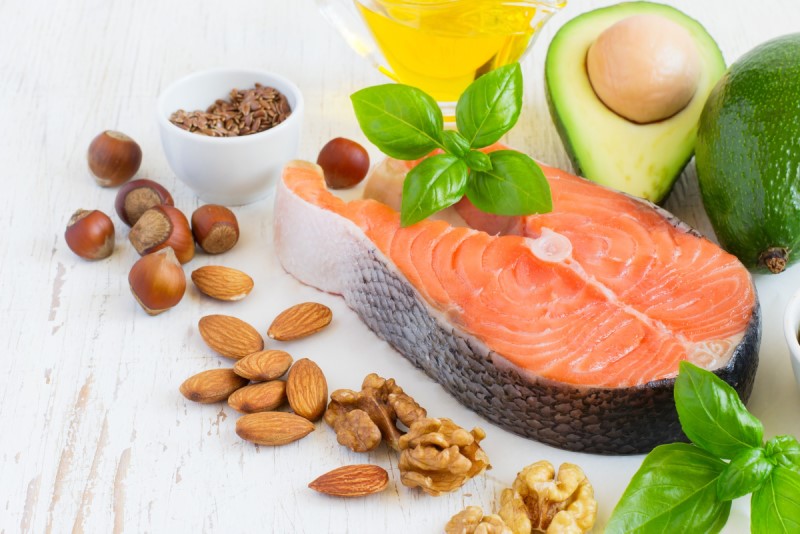
The management of lipid intake is another important factor. It is advised to limit saturated fats, found in foods of animal origin, in order to favor unsaturated fats, found in nuts, avocados and vegetable oils such as olive oil. Unsaturated fats are beneficial for cardiovascular health, which is particularly beneficial for people with diabetes.
The article also emphasizes the need for portion control and a well balanced meal distribution throughout the day. Eating at regular intervals is recommended to keep blood glucose levels stable. In addition, the article mentions that blood glucose monitoring with a glucometer is an essential tool for adjusting the diet to suit individual needs.
Besides nutrition, the article underlines the pivotal role of patient education in diabetes. Individuals with diabetes need to be well informed on how to read nutrition labels, count carbs and understand the glycemic index of foods.
In a nutshell, nutrition plays a fundamental role in diabetes management. Basic recommendations include carbohydrate and fat monitoring, portion moderation, balanced meal planning and diabetes education. By following these guidelines, people with diabetes can more effectively control their blood glucose levels and maintain optimum health in the long term.
Reference:
- Article source: Nutrition Principles and Recommendations in Diabetes Care