Diabetes is an increasingly common medical condition that can have serious health consequences. However, recent scientific studies suggest that a powerful weapon in the management of diabetes may be more achievable than you thought: physical exercise.
Overview of diabetes
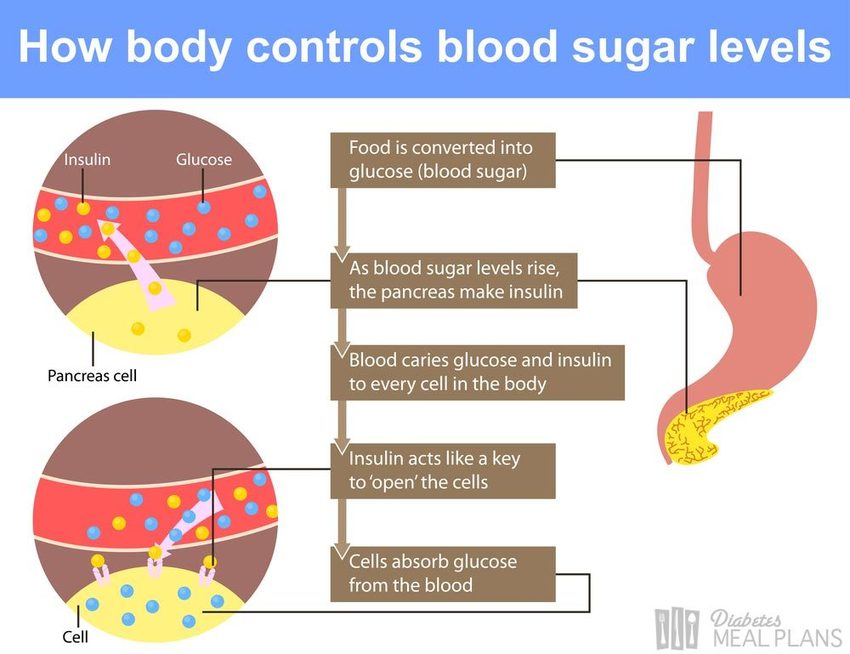
Diabetes is a chronic disease characterized by high blood sugar levels. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1, which is usually diagnosed in young people and is autoimmune in origin, and the more common type 2, which is often associated with a sedentary lifestyle and obesity.
The benefits of exercise
Regular exercise offers many benefits for people with type 2 diabetes and can even prevent its development in those at risk. Here are some of the key benefits, based on scientific research:
1. Improved insulin sensitivity: A study published in the journal “Diabetologia” showed that regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, enabling the body to use sugar more efficiently, lowering blood sugar levels and reducing the need for medication.
2. Weight control: Obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes. Exercise helps burn calories and maintain a healthy body weight.
3. Abdominal fat reduction: Abdominal fat is particularly linked to type 2 diabetes. A study published in the “Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” showed that exercise reduces visceral fat, which is beneficial for diabetics.
4. Blood sugar control: According to a study by the National Center for Biotechnology Information, regular exercise can help maintain stable blood sugar levels by increasing the muscles’ ability to use glucose.
The Key to success: consistency
It’s important to note that to reap the full benefits, exercise must be regular. A single intense workout is not enough. Experts recommend aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, spread over several days.
Conclusion
Regular exercise can be a powerful ally in the management of type 2 diabetes. Combine this with a balanced diet and appropriate medical follow-up, and it’s possible to live a healthy, active life despite diabetes.
Références :